Are you a new rider and wondering what the different parts of the horse saddle are called? Or a more experienced rider who wants to learn more about horse saddle parts and their functions? Then this article is right for you, in this blog post I will help you understand the most important parts of the saddle and the basics of different saddle types.
- Basic about the Horse Saddle
- Parts of the English Saddle
- Pommel
- Gullet
- Cantle
- Seat
- Twist or Waist
- Skirt or Jockey
- Flap
- Knee Roll, Knee Block, or Knee Pads
- Calf block
- Stirrup Leather
- Stirrup
- Stirrup Bar
- Stirrup Leather Keeper
- Sweat flap
- Panels
- Girth
- Girth straps, billets, or billet straps
- Buckle guard or billet guard
- D-ring, Staple, or Breastplate Dee
- Saddle nail
- Ring to attach croup straps
- The Saddle Tree
- Parts of the Western Saddle
- Swell or Pommel
- Gullet
- Horn
- Seat
- Seat Jockey
- Cantle
- Back Jockey, Rear Jockey, or Housing
- Skirt
- Front Rigging Dee
- Rear Rigging Dee
- Saddle Strings
- Back Billet or Flank Billet
- Latigo
- Front Cinch
- Back Cinch or Rear Cinch
- Stirrup
- Stirrup Leather, Blevin Strap, or Adjustment Strap
- Fender
- Hobble strap
- Latigo Keeper
- The Bars
- The Tree
- Saddle Terms English vs Western
- Different types of saddles
Basic about the Horse Saddle
The saddle is the piece of equipment laying on the horse’s back where the rider sits. The saddle has been developed to ease the riding of horses. The saddle can be made of different materials, usually leather or synthetic materials. The saddle must fit both the horse and the rider to make the riding experience pleasant and comfortable. The saddle is built with individual parts by saddle makers. The size of the saddle should fit both the horse and the rider. There are different saddles for different purposes and riding styles. Different saddle types look different and to some extent have different parts.

Parts of the English Saddle
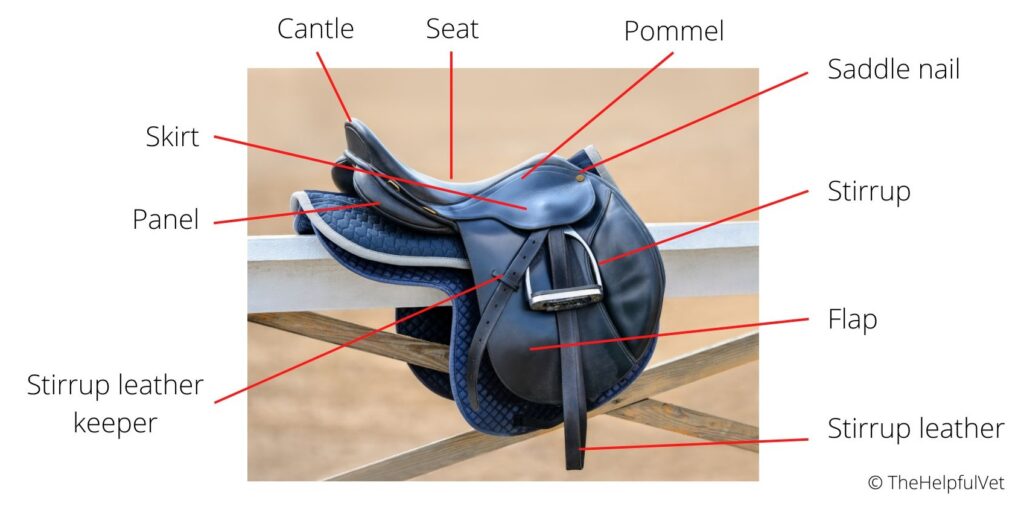

Here is a list of common parts of an English saddle explained with function and pictures.
Pommel
- The Pommel is the highest part of the front saddle.
- It prevents the rider from moving forward.
- This part needs to fit the horse’s back and withers.

Gullet
- Under the pommel
- The channel runs on the underside of the saddle between the panels.
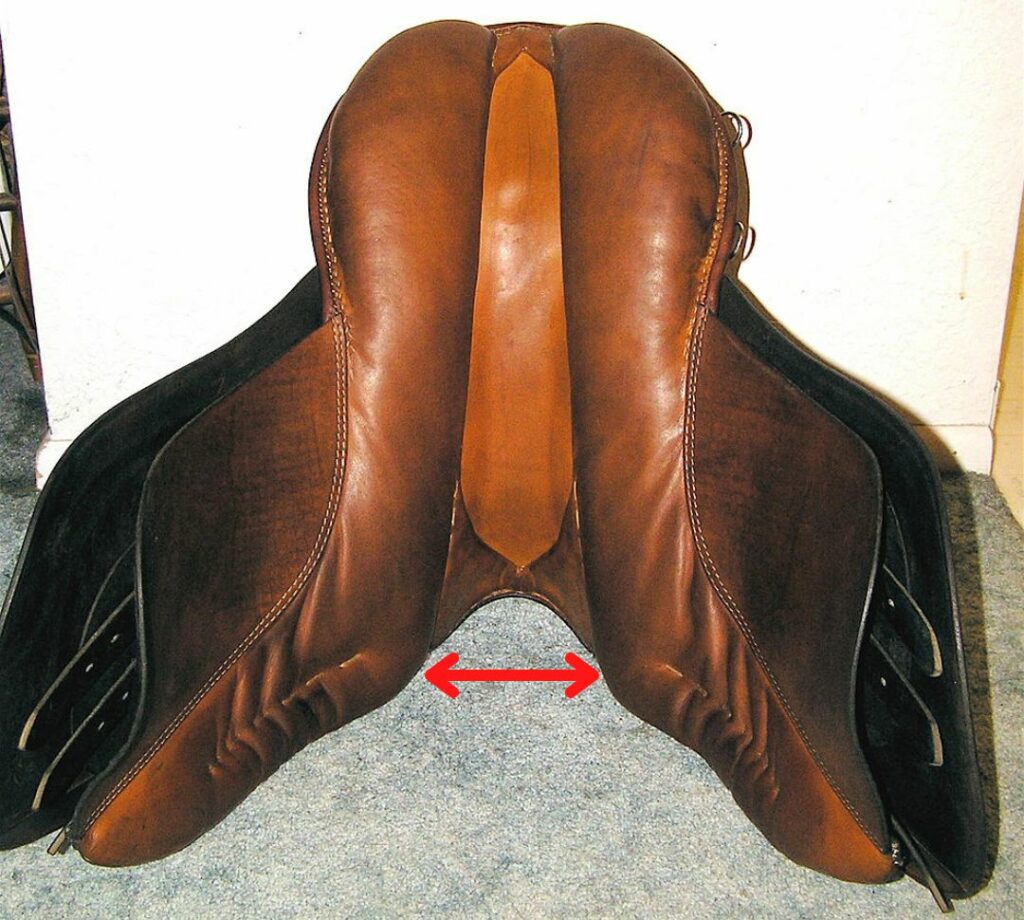

Photo: BLW, CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/, via Wikimedia Commons
Cantle
- The cantle is the highest point of the saddle and is placed in the back of the seat.
- The cantle keeps the rider in a safe position not falling backward
- Higher cantle and more vertical cantle in dressage saddles.
- More round and skewed cantle in jumping saddles

Seat
- Middle deeper point of the saddle, between the pommel and cantle
- Should fit the rider
- 16’’-16,5’’ for small riders
- 17-17,5’’ for medium size riders
- 18”’-19” for larger riders
- Jumping saddles have more flat seats
- Dressage saddles usually have deeper seats

Twist or Waist
The twist is the narrowest part of the seat.

Skirt or Jockey
Small piece of leather which covers the stirrup leather fastener.

Flap
- Leather flaps on both sides of the saddle covering the girth and girth straps
- Protects the rider’s legs and horse´s side from rubbing against each other
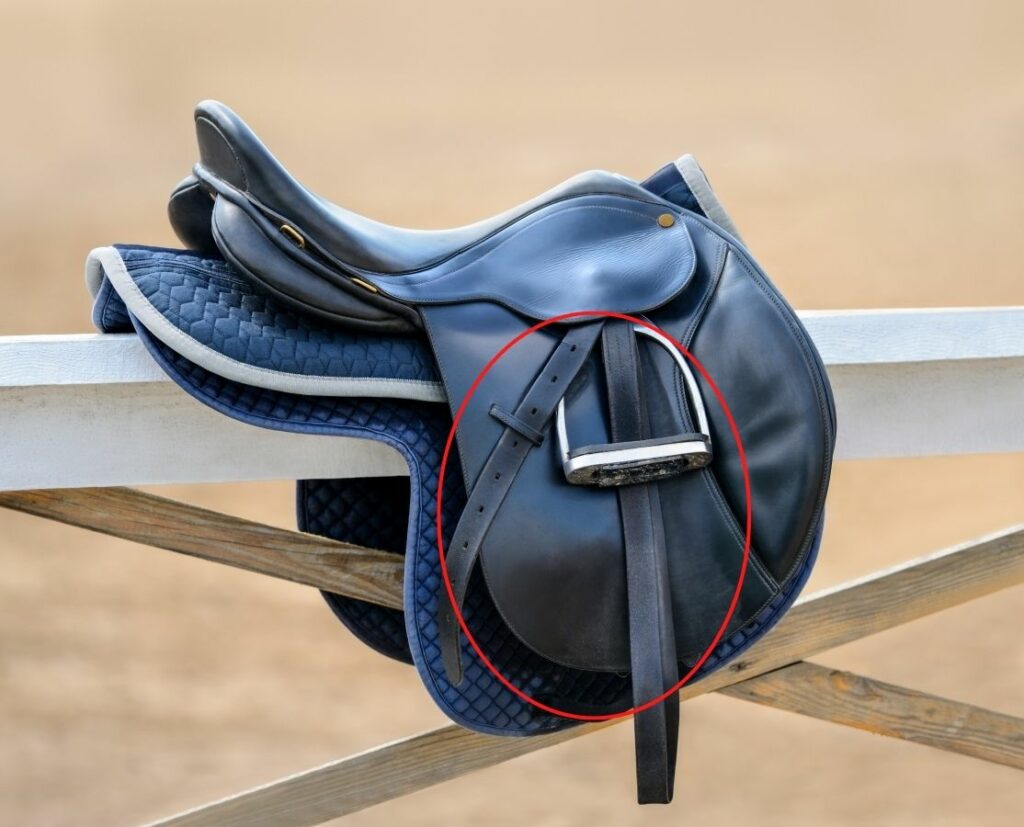

Knee Roll, Knee Block, or Knee Pads
The padded part at the front of the saddle. Gives the rider more or less leg support according to size.

Photo: BLW, CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/, via Wikimedia Commons
Calf block
A padded part at the back of the saddle. Gives the rider more or less leg support according to size
Stirrup Leather
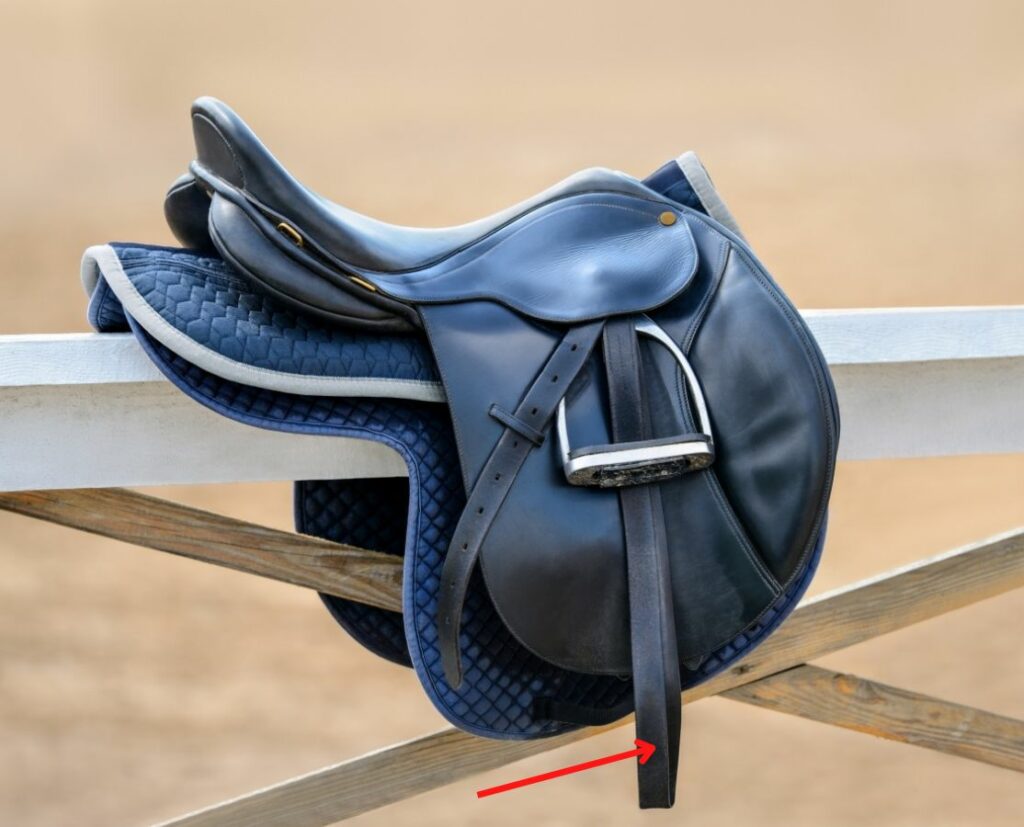

- Piece of leather (or synthetic materials) strap holding the stirrup.
- Is placed in the stirrup bar.

Photo: “Stirrup leathers, brand new, 55′, $65” by jenniferdukedodd is licensed under CC BY 2.0.
Stirrup
- A metal or plastic frame used to put the rider’s foot in, both when mounting the horse and when riding.
- Comes in different shapes and models, some focusing on safety and others on looks.
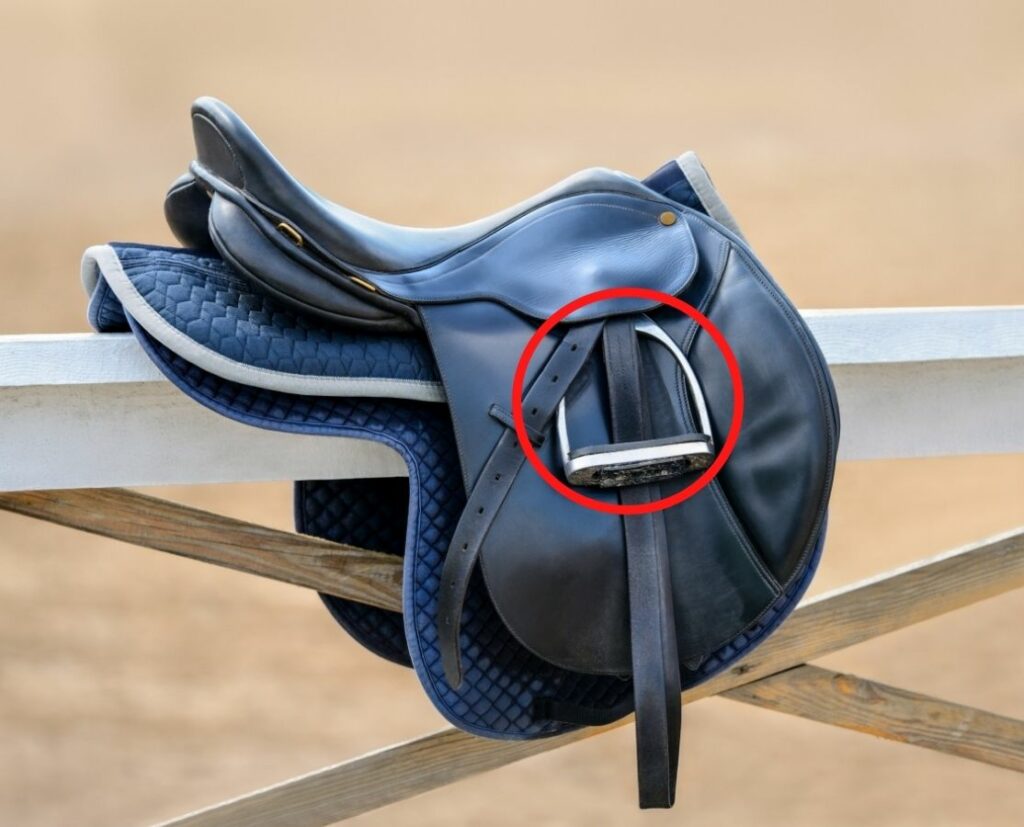

Stirrup Bar
- The stirrup bar is a holder for the stirrup leather
- The stirrup bar is located under the jockey
- The Stirrup bar can be equipped with a safety hinge which, when left open, allows the stirrup leathers to slide out in case the rider falls off and gets stuck in the stirrup. This prevents the rider from being dragged behind the horse.

Photo: Montanabw, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Stirrup Leather Keeper
- A piece of equipment holding the stirrup steady and covering the buckle if positioned by the rider’s ankle.
- The definition can also be used on the small leather strap that holds the excess stirrup leather in place on the back of the saddle flap.

Sweat flap
The part of the saddle on the sides laying closest to the horse.

Photo: BLW, CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/, via Wikimedia Commons
Panels
- Two cushions underneath the saddle that distribute the rider’s weight.
- The two panels leave a space in between them making room for the horse’s spine.
- Different types of padding for the panels:
- Latex
- Sweat flapWool (synthetic or natural)
- Foam
- Felt
- Air
- Combinations of above
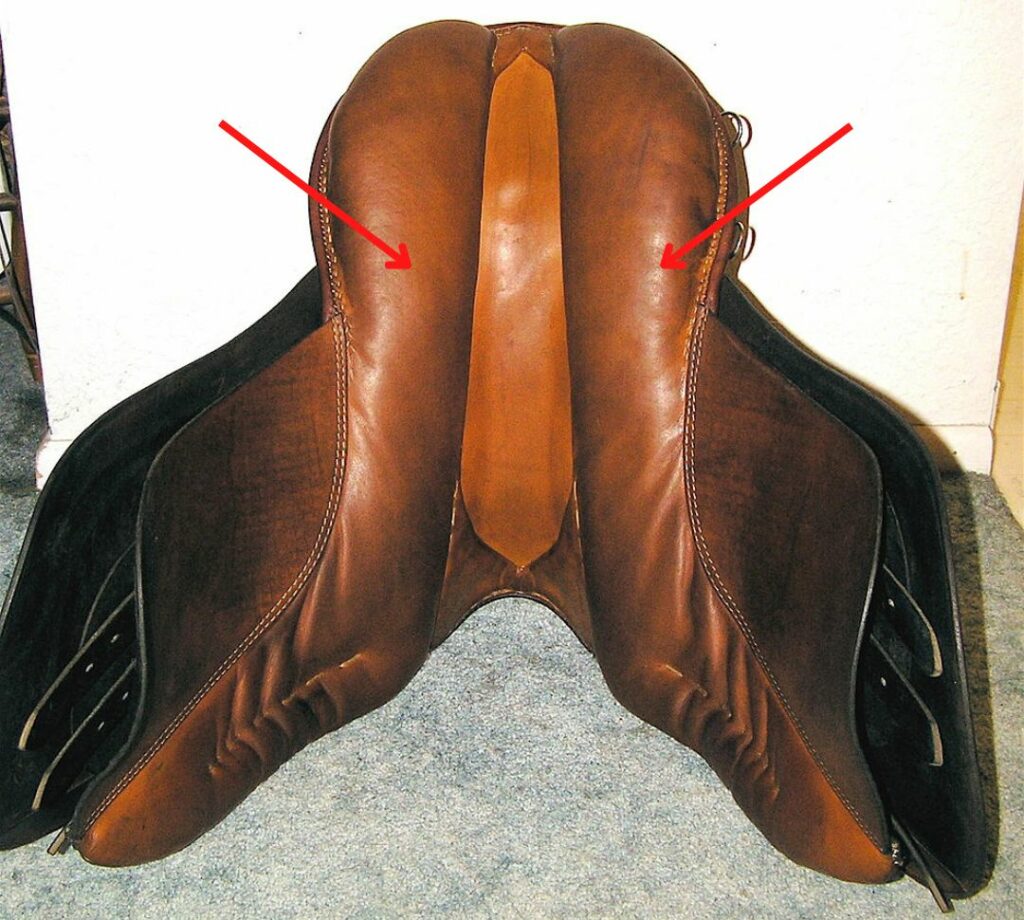

Photo: BLW, CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/, via Wikimedia Commons
Girth
- The Girth is a piece of equipment holding the saddle in place. Is fastened in the girth straps in the saddle on the horse’s sides and passes under the horse’s belly.
- Comes in different models and materials.
- A dressage saddle has a shorter girth than a jumping saddle.
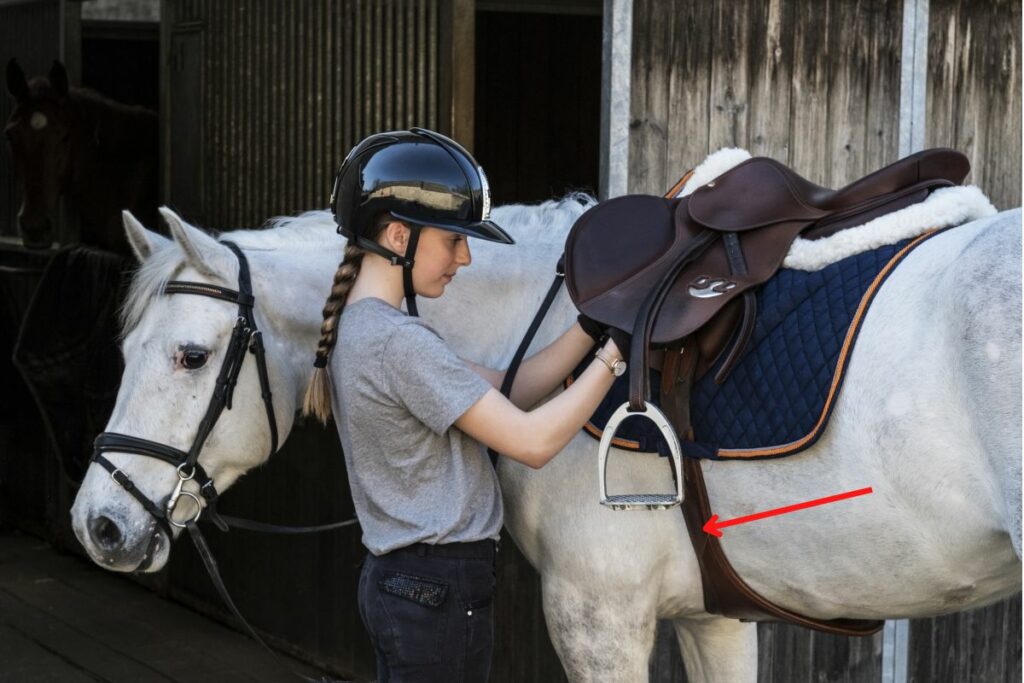

Girth straps, billets, or billet straps
- Straps for attaching the girth on both sides of the saddle
- All-purpose saddles and jumping saddles usually have three straps on each side. The straps are hidden under the flap
- Dressage saddles usually have two straps on each side. The straps are longer and extend out of the outline of the saddle.

Photo: BLW, CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/, via Wikimedia Commons
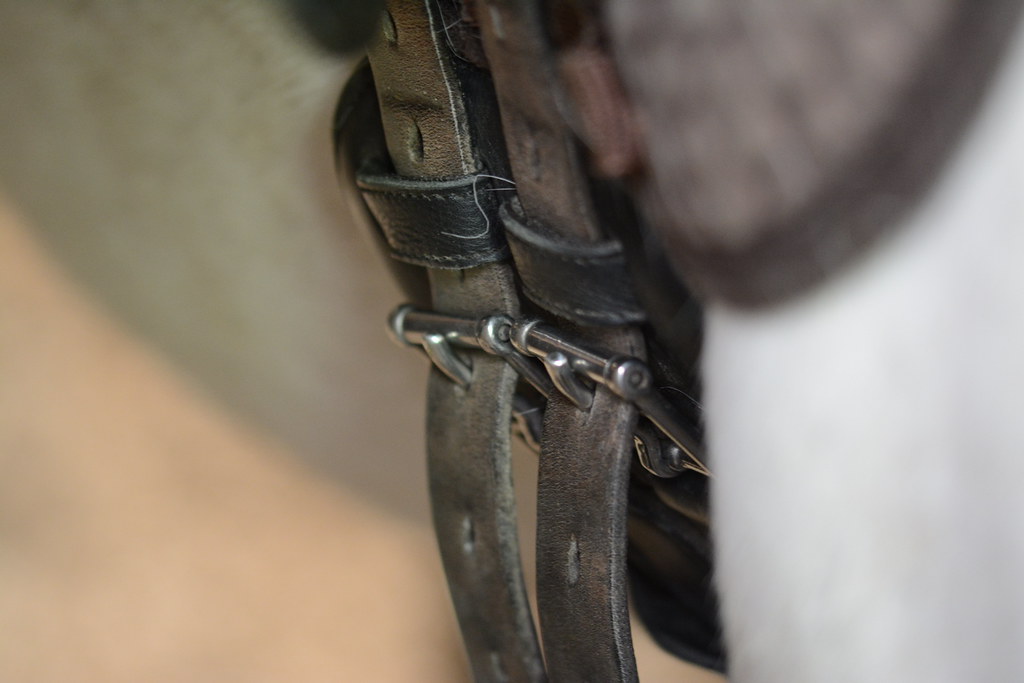

Photo: “Girth Straps” by Clint__Budd is licensed under CC BY 2.0.
Buckle guard or billet guard
Leather flap protecting the saddle flap from the buckles of the girth.

Photo: BLW, CC BY-SA 3.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/, via Wikimedia Commons
D-ring, Staple, or Breastplate Dee
Metal ring for attaching equipment i.e. breast collar.

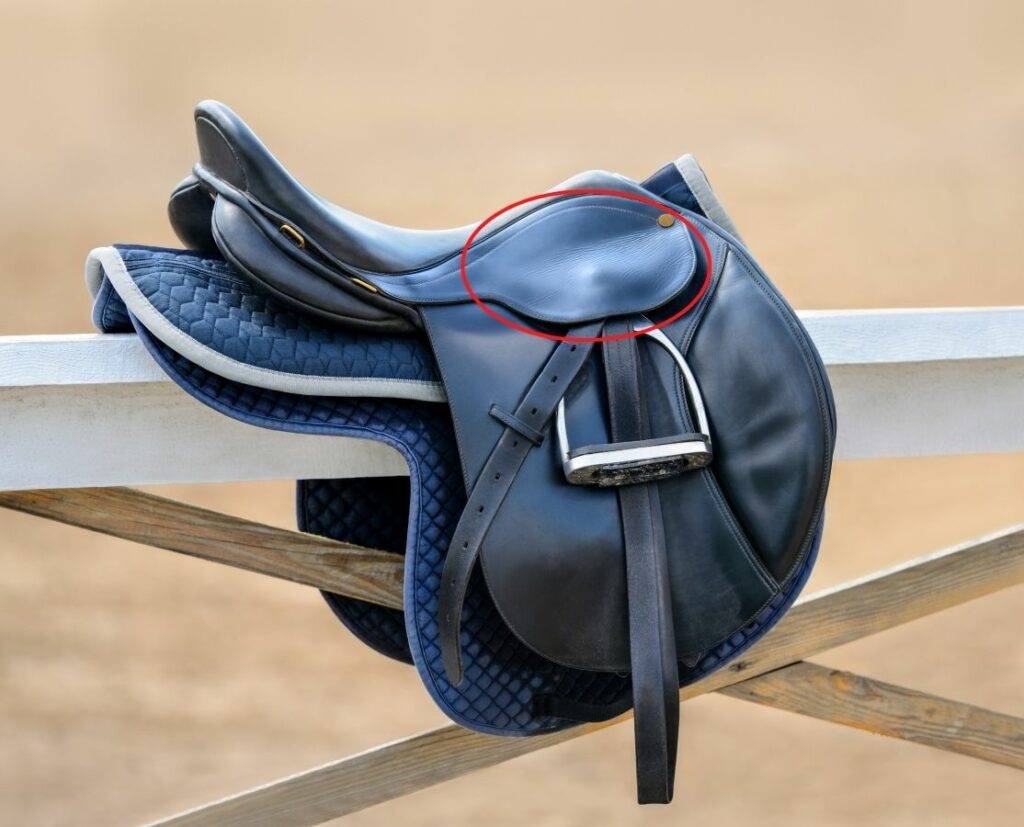
Saddle nail
- The saddle nail attaches the skirt and flap to the tree.
- Located on the side of the pommel.

Ring to attach croup straps
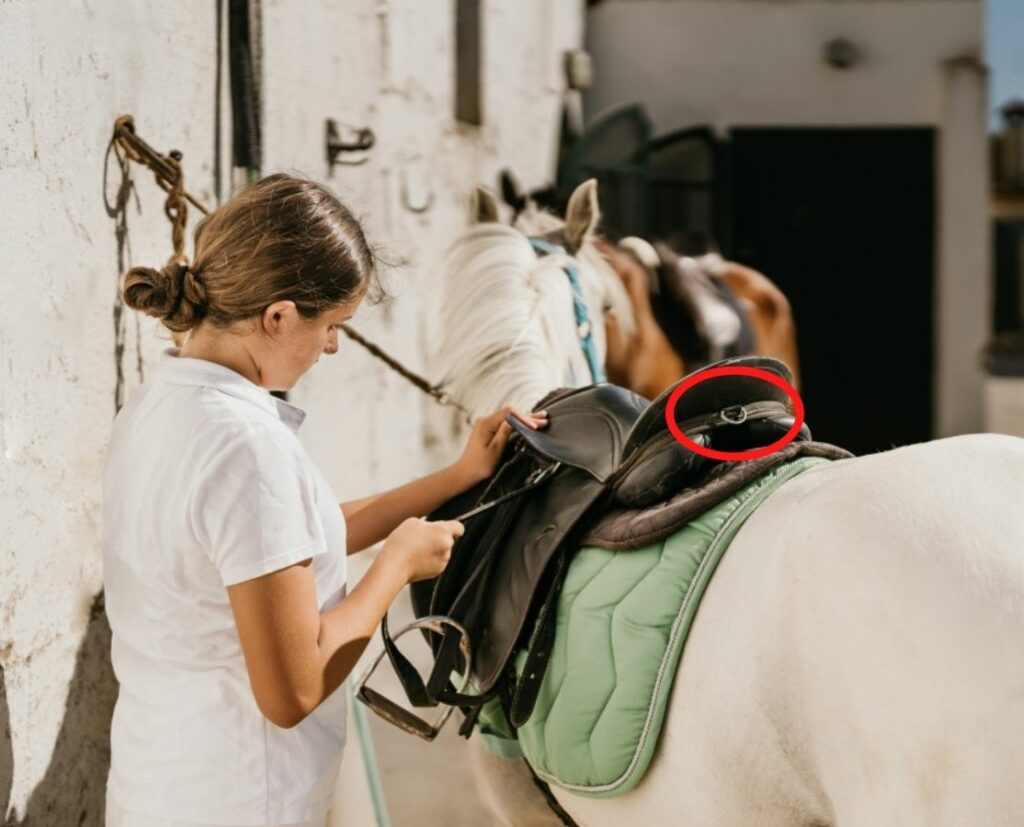
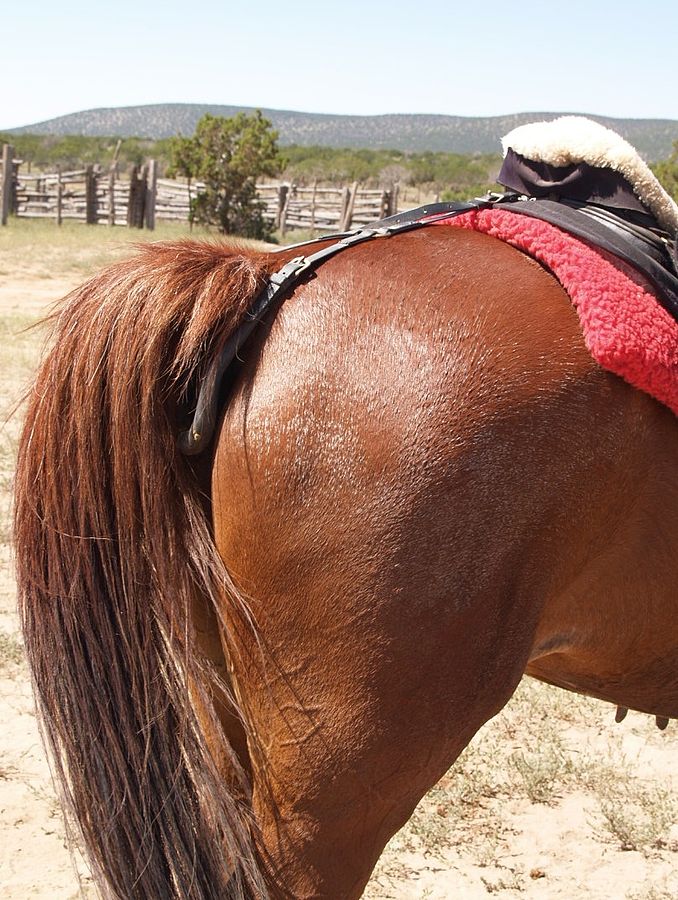


Photo: Una Smith, CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The Saddle Tree
- Part of the saddle you can’t see without taking it apart.
- The main part, the backbone, of the saddle which plays an important role and determines the shape of the saddle
- Made of different materials
- Formerly always made of wood
- Synthetic material i.e. fiberglass (doesn’t deform and is lightweight)

Photo: ThatPeskyCommoner, CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Parts of the Western Saddle
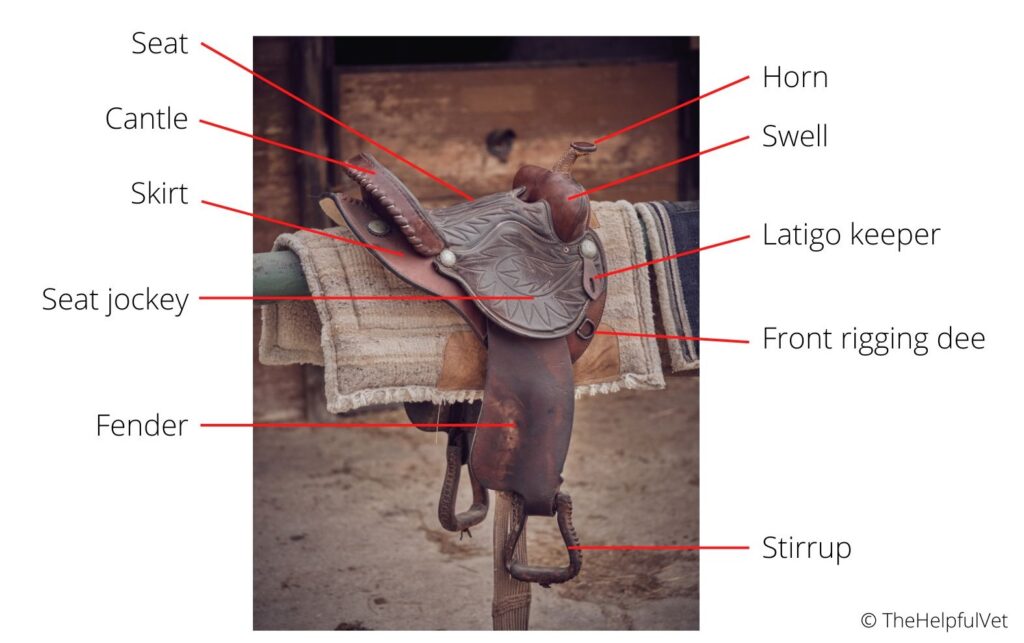
Here is a list with pictures and descriptions of different parts of a western saddle.
Swell or Pommel
- Also called pommel
- The high part in front of the saddle.
- The upper part of the gullet.

Gullet
- A tunnel placed over the horse’s withers.
- Important part of the saddle holding the bars of the saddle together.
- The angle of the gullet and the gullet height must fit the specific horse

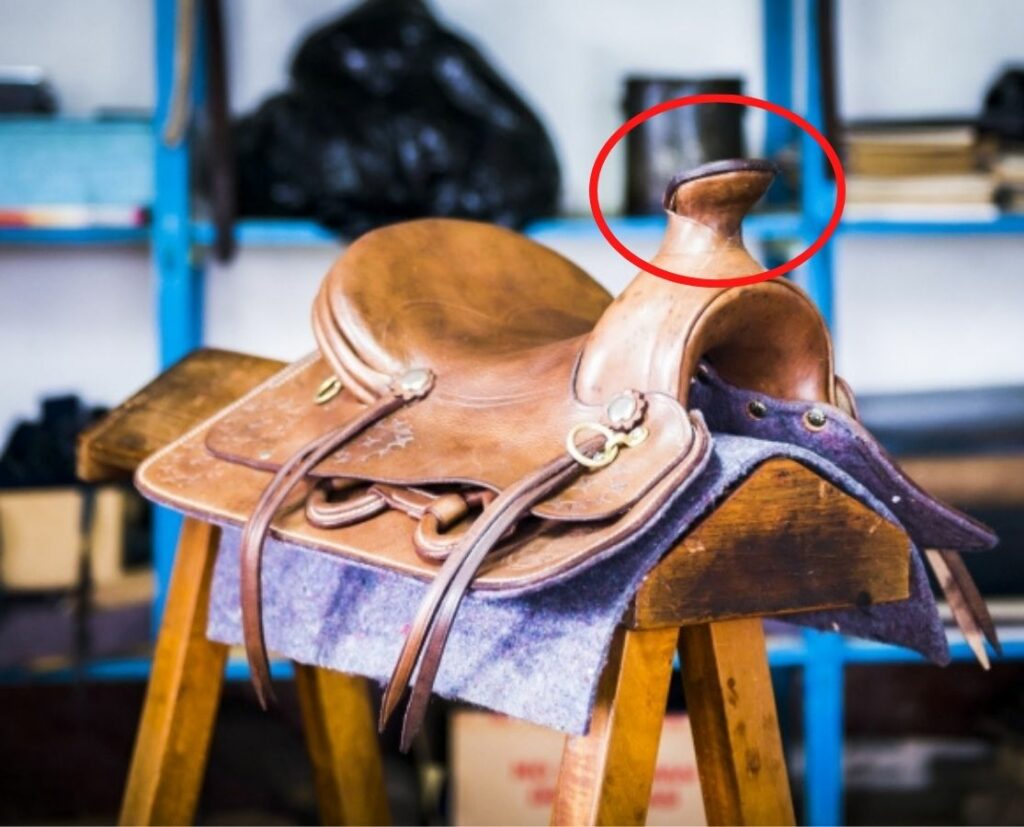
Horn
- The saddle horn can be used to hold on to but is originally formed to wrap a rope around.
- It is placed on the swell on top of the saddle.

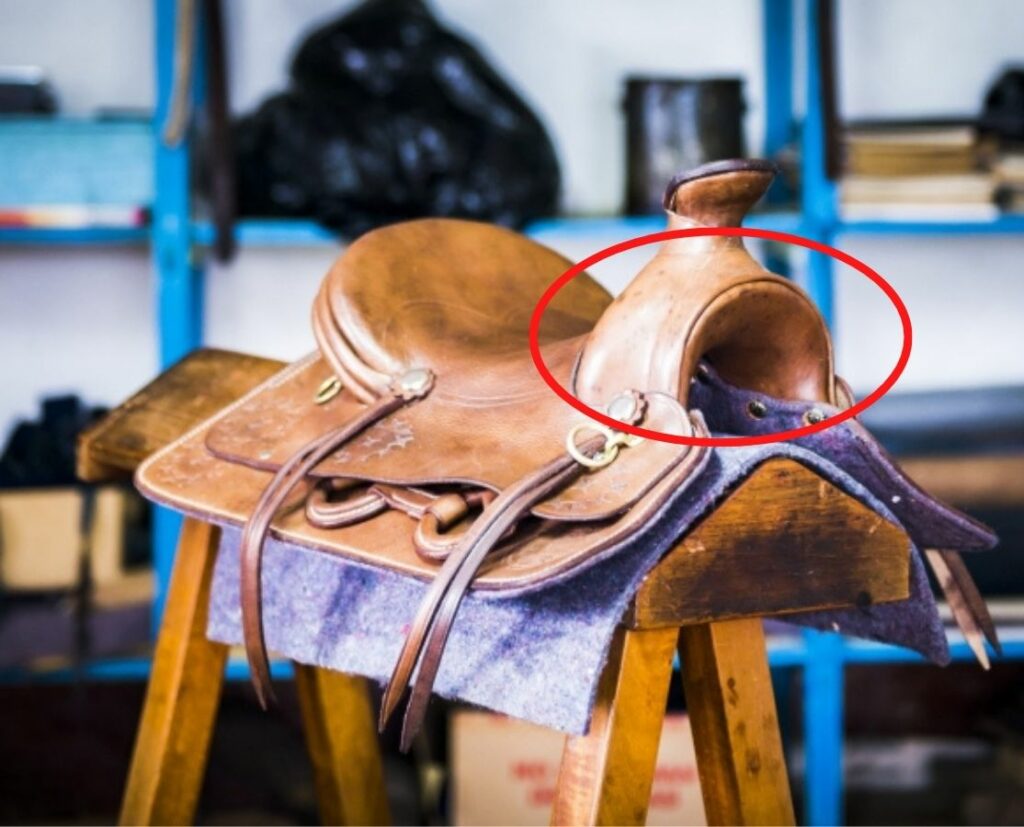
Seat
- Middle deeper point of the saddle, between the pommel and cantle
- The slope of the seat, varies and the seat can be either hard or soft.
- Most often in leather
- Western saddles come in different sizes and a variety of seat sizes. The rider’s seat should fit the saddle seat.

Seat Jockey
- Protective leather flap on both sides of the saddle. They are extending from the edges of the seat.
- The seat jockeys are often decorated.
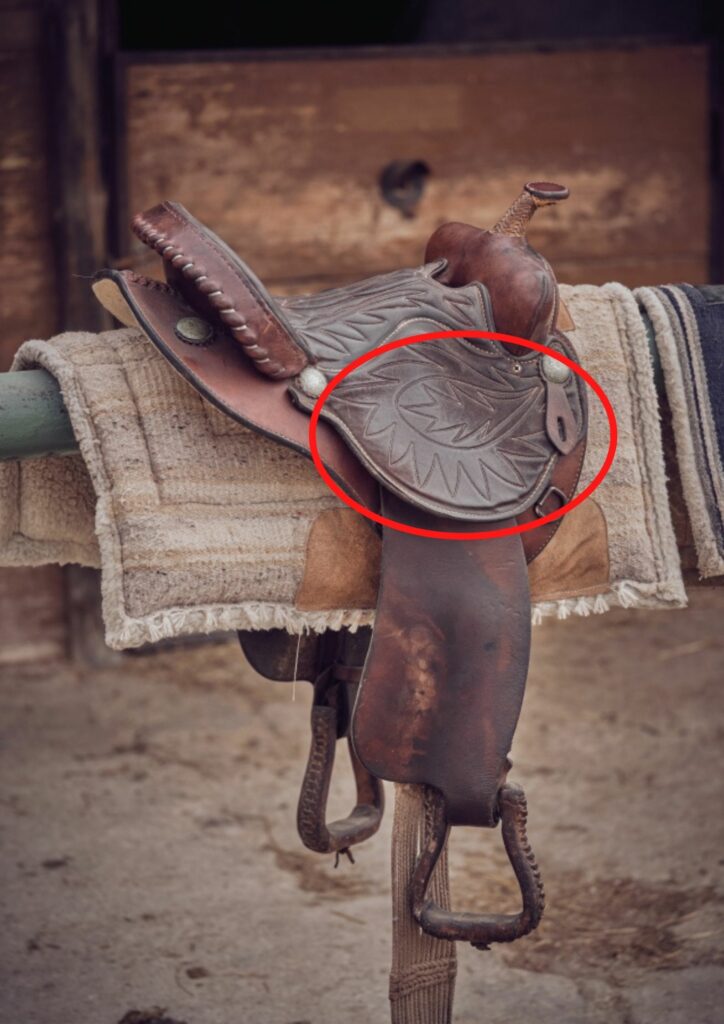

Cantle
- Hight part on the rear end of the saddle.
- The cantle comes in different styles:
- Cheyenne Roll: leaving open spaces, “lip” under the cantle which can be used to fixate an item under.
- Pencil roll: gives a more cupped look
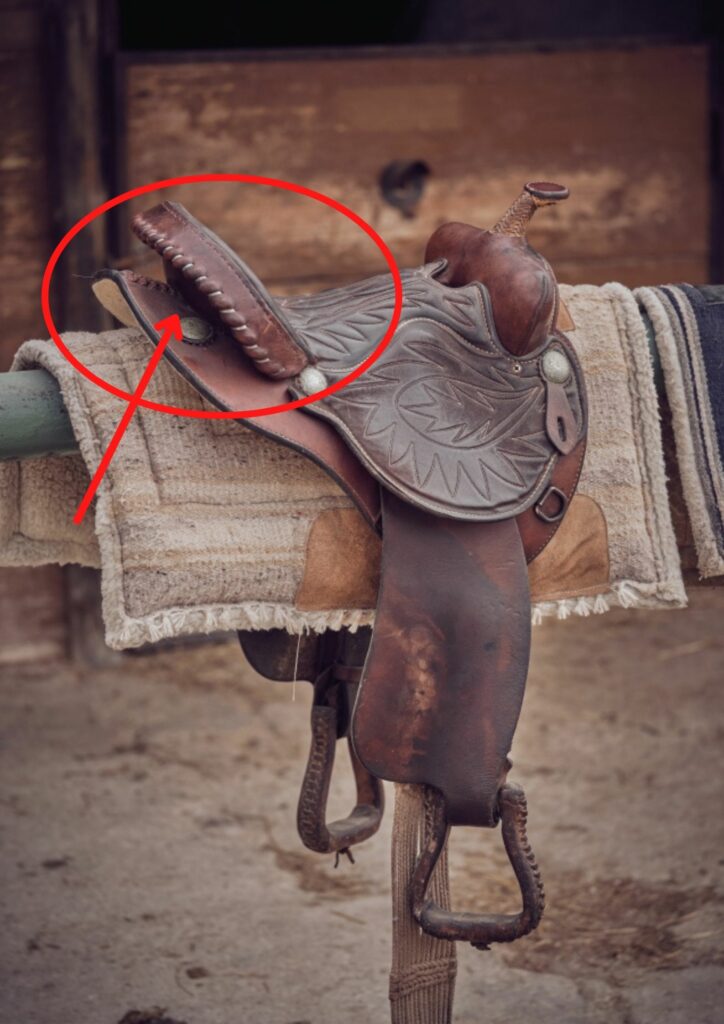

Back Jockey, Rear Jockey, or Housing
- Leather piece extending backward from the sides of the seat and the cantle
- Some saddles come without back jockeys, usually to cut down on the weight of the saddle.
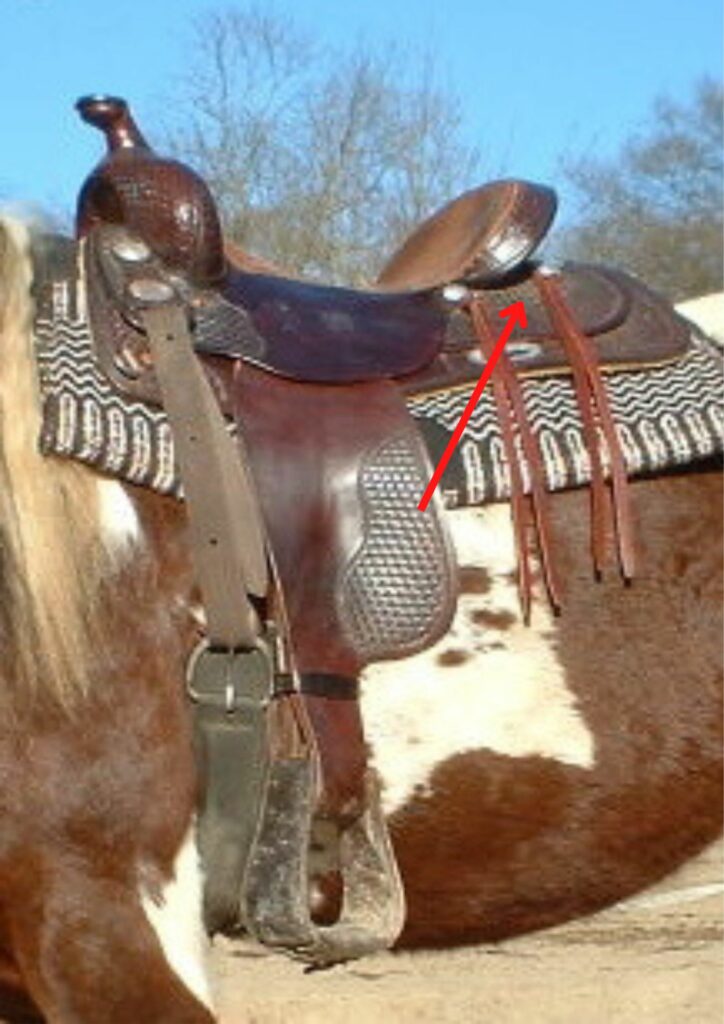

Skirt
- The Skirt is a large piece of leather underneath the tree of the western saddle.
- It is often decorated and seen around the sides and at the back part of the saddle.
- The skirt can be rounded or squared-shaped.

Front Rigging Dee
- Large D-rings in the front of the saddle fastened in the tree.
- The purpose of the rings is to attach the cinch via the latigos.
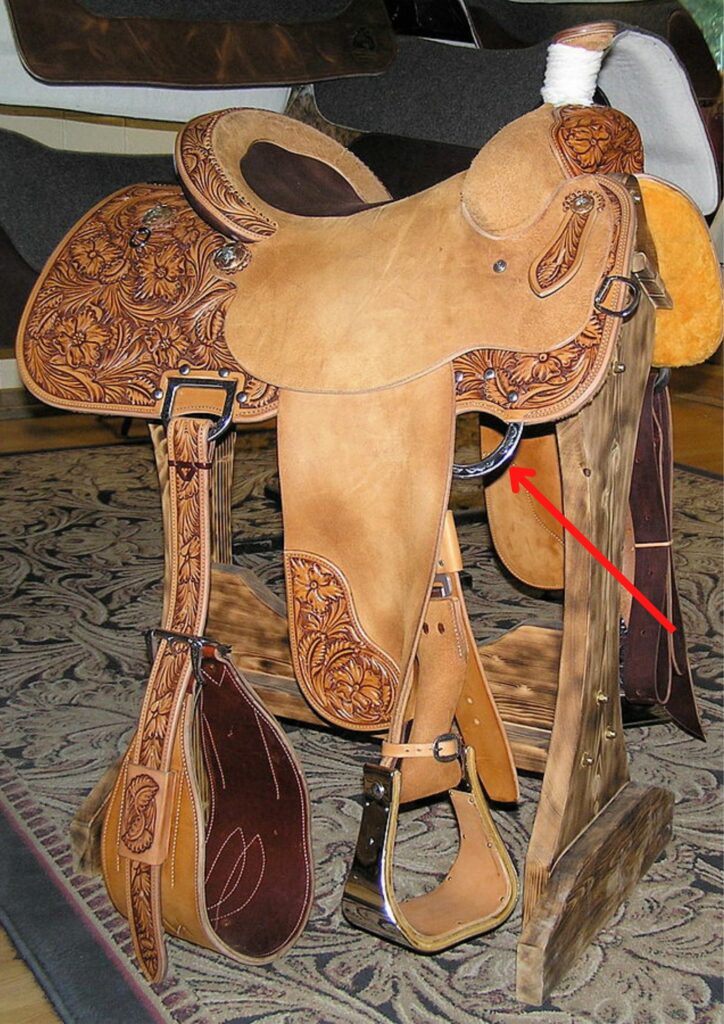

Photo: Montanabw, CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Rear Rigging Dee
- Like the front rigging dee the back rigging dee is attached to the tree.
- The rear rigging D-ring is placed below the cantle at the rear of the saddle.
- The purpose of the ring is to fasten the flank billet and connect the back cinch.

Photo: Montanabw, CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Saddle Strings
Strings of leather are fastened to the western saddle and are both decorative and functional. The saddle strings are used to tie things to the saddle.

Back Billet or Flank Billet
- Tough leather lengths fastened in the rear rigging D-rings
- Used to fasten the back cinch

Photo: Montanabw, CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Latigo
- Cinch connecting strap or Latigos
- Long thick leather or synthetic strap with holes in, to connect the cinch with the western saddle.
- The Latigo is attached to the front rigging dee.

Front Cinch
- The cinch is keeping the horse stable on the horse. It passes from one side of the horse under the belly to the other side of the horse, fastened in the latigos.
- Comes in different materials i.e. mohair, neoprene, and fleece.

Back Cinch or Rear Cinch
- This second cinch is placed further back on the saddle compared to the front cinch.
- Makes the saddle more stable, especially when horses are going up and downhill.

Stirrup
- The stirrup is the piece of equipment where the rider keeps their feet during riding.
- The stirrups are made of different materials wood, metal, plastic, or leather.

Stirrup Leather, Blevin Strap, or Adjustment Strap
- Leather strap with holes behind the stirrup fender
- Make the length of the stirrups adjustable
- The stirrup leather is attached to the tree

Photo: Montanabw, CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Fender
- Leather panels, often decorated, covering the stirrup leather
- The fender is connected to the stirrup leather

Photo: Montanabw, CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Hobble strap
A small leather strap placed just above the stirrup keeps the fender leather together
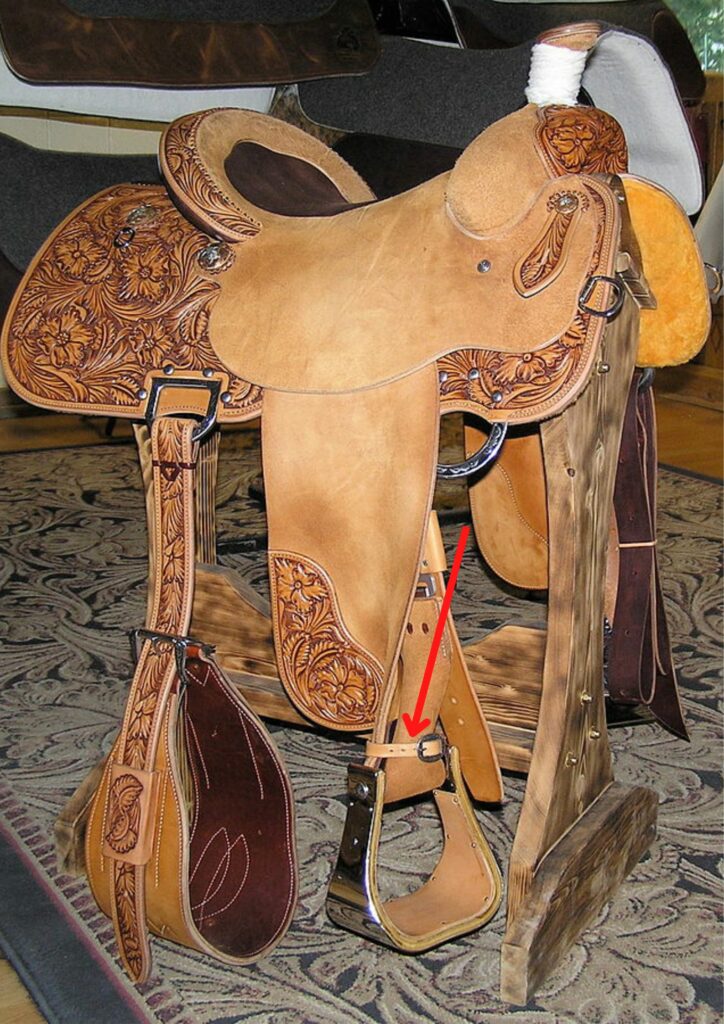

Photo: Montanabw, CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Latigo Keeper
- Triangular piece of leather at the base of the swell on each side of the saddle.
- The latigo keeper’s function is to secure the loose tail of the latigo

The Bars
- The bars are connected in the front by the swell and then extend backward following each side of the horse’s spine creating a pressure-free tunnel.
- Divides the weight of the rider and saddle evenly on the horse
The Tree
- The tree is the backbone of the saddle and it is not visible without taking the saddle apart.
- This important part of a saddle gives shape to the gullet, horn, swell, bars, and cantle.
- Made of wood i.e. western pine (known as the best wood), or synthetic material i.e. glass fiber.
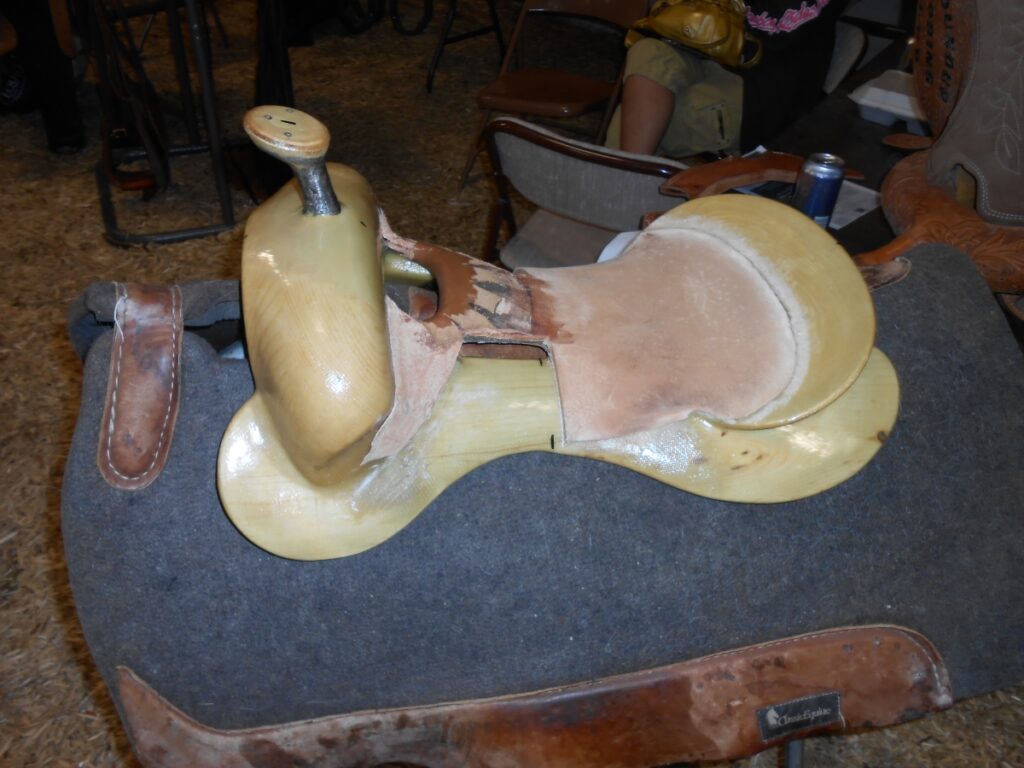

Photo: “File:Western saddle tree 1.JPG” by Montanabw is licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0.
Saddle Terms English vs Western
| English Saddle Term | Western Saddle Term |
|---|---|
| Girth | Cinch |
| Pommel | Swell |
| Girth billet | Latigo |
| Panels | Bars |
| Flap/stirrup leather | Fender |
Different types of saddles
Different types of saddles are used for different purposes. These saddles are constructed differently with different parts. The two most common types of saddles are the English saddles and the Western saddles. Then there are also other types of saddles for horse riding i.e. racing saddles and Treeless Saddles. The type of saddle you choose depends on what riding style you are into.
English saddle
Used for English riding and comes in different styles.
- General Purpose Saddle
- Used mainly for pleasure riding and recreational riding.
- The general-purpose saddle is comfortable for long rides and basic purposes.
- Deeper saddle seat, round cantle, and knee rolls

Photo: “Item 34 Saddle, all-purpose style with cutback pommel, 17-and-one-half inches, Coventry Commander, left side” by KJSchrage is marked with Public Domain Mark 1.0.
- Dressage Saddle
- The stirrup bars are directly under the seat of the rider
- Deep seat, high and round cantle. The dressage saddles have long straight flaps suitable when the rider sits upright with long stirrup leathers.
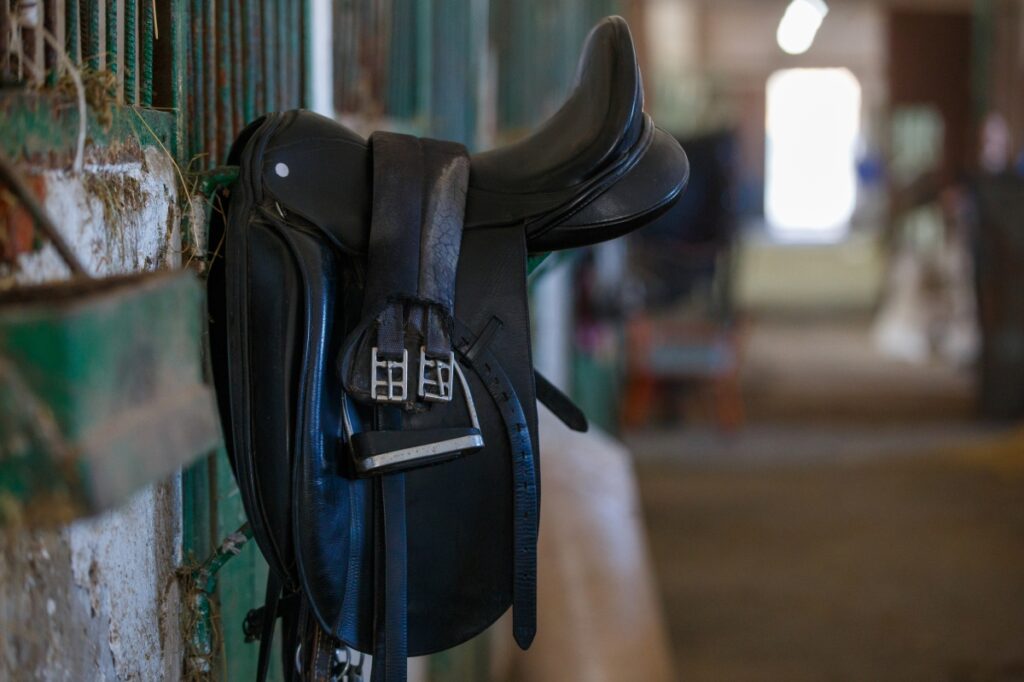

- Jumping Saddle
- Rather flat saddles
- Constructed for jumping and is often close contact saddles.
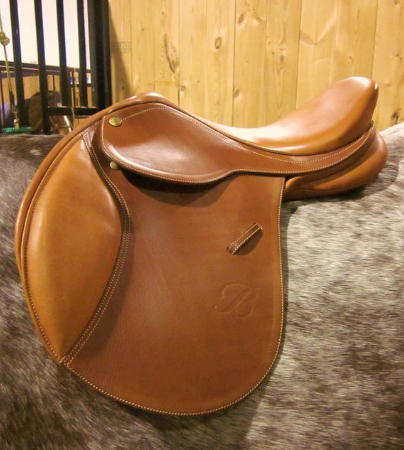

Photo: “File:Bates Caprilli Close Contact Saddle.png” by Danielle M. is licensed under CC BY 3.0.
- Hunting Saddle
Saddles made for hunting.

Photo: “Prince Albert’s Hunting Saddle c.1850” by Matt From London is licensed under CC BY 2.0.
Youth Saddle
- The first saddles used by beginner riders of small size.
- Often with grab straps in the front to hold on to.
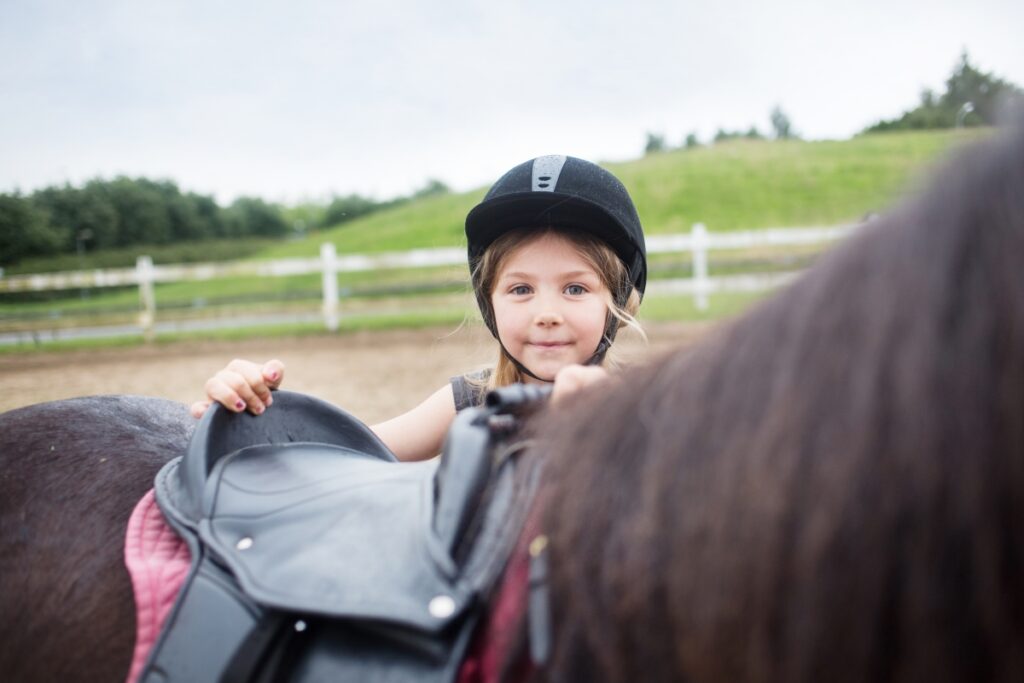

Western Saddle
- Used for western riding.
- There are different types of western saddles according to what discipline you are into i.e. barrel racing saddles.
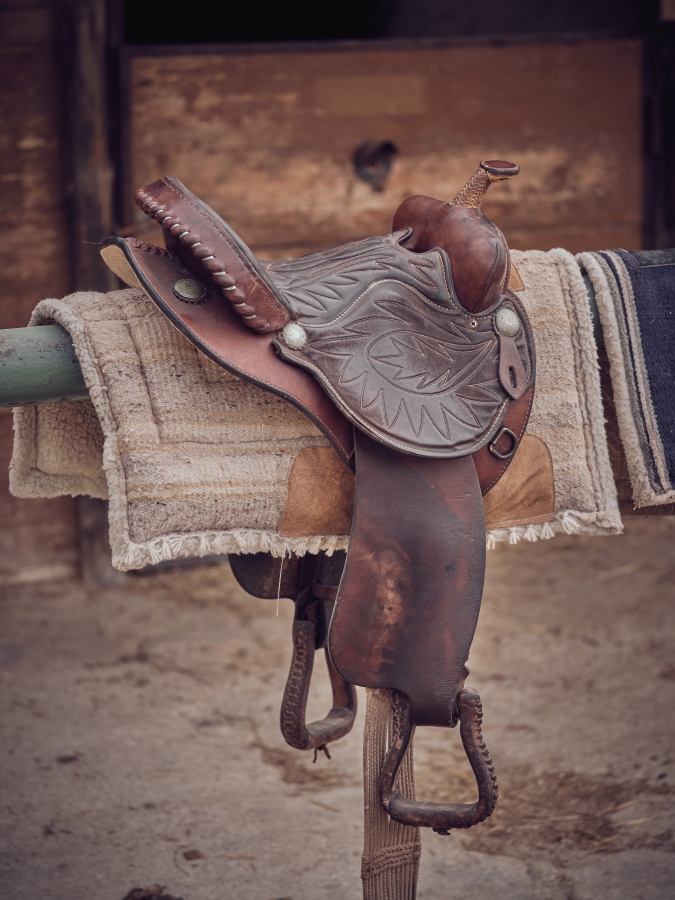

Side Saddle
- Old saddle that historically allowed female riders to sit aside.
- Side saddles are still used to some extent.
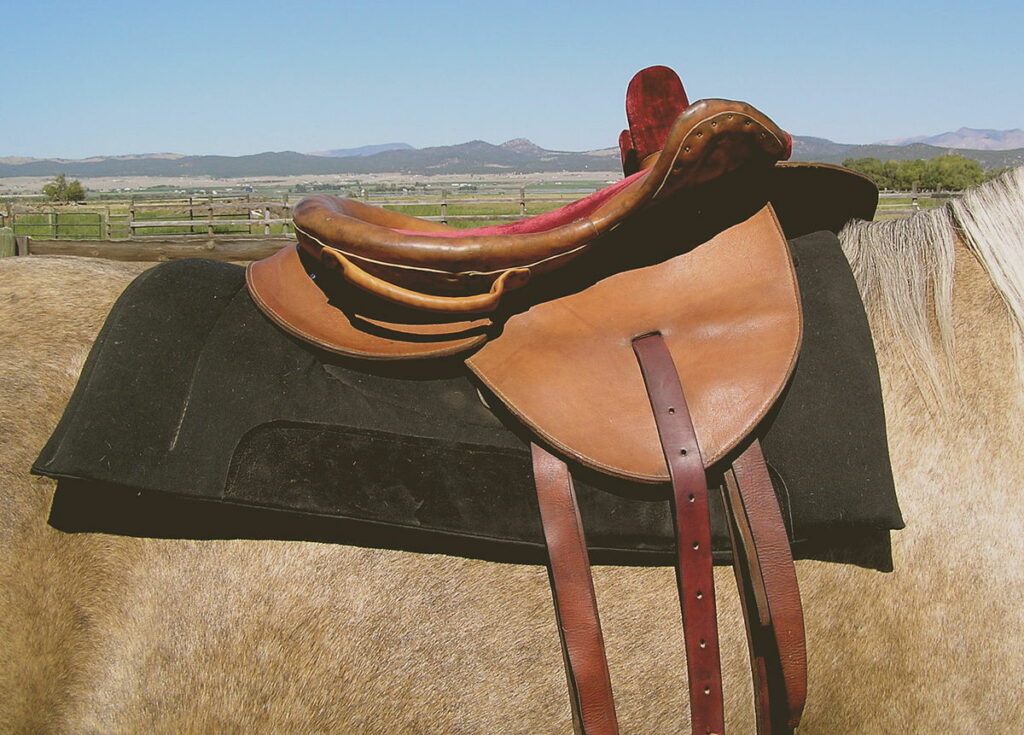

Photo: Montanabw, CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Racing Saddles
Very thin and light saddles adapted for fast horse racing.
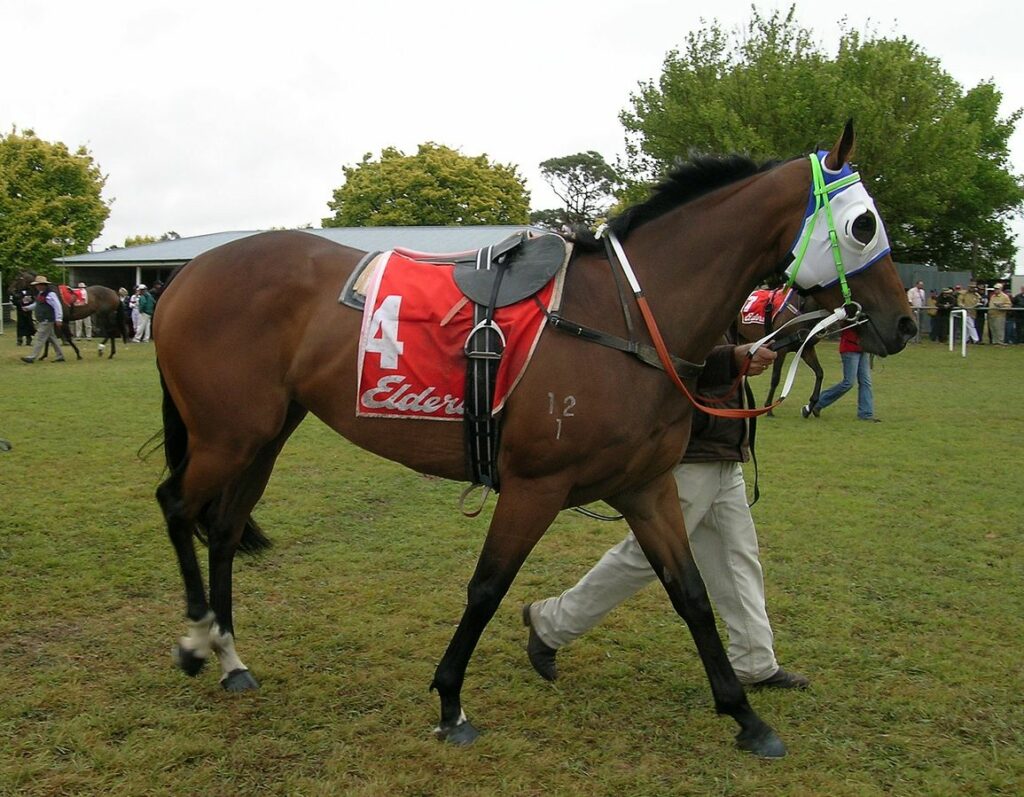

Photo: User:Cgoodwin, CC BY-SA 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Treeless Saddle
Saddle without the tree. Some people claim treeless saddle to be more natural and make the rider gets closer contact with the horse.
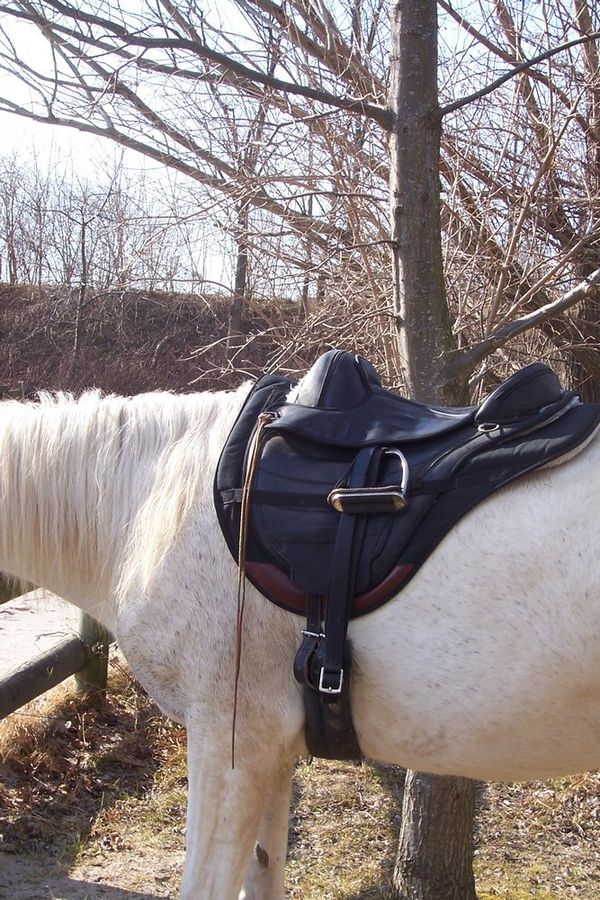

Photo: Alex brollo, CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0, via Wikimedia Common
Australian Stock Saddle
Australian saddle was adapted for example long rides, cattle work, and pleasure riding.

Photo: ThatPeskyCommoner, CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
I hope this article was helpful in teaching you a lot about the different parts of the saddle as well as the different types of saddles.

